April 10, 2019
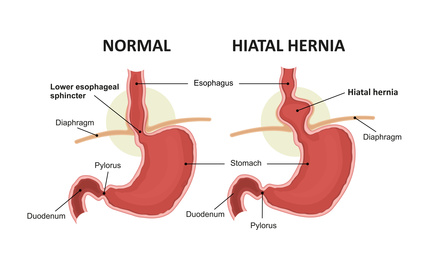
Hiatal hernia, sometimes called “esophageal hernias”, is a condition characterized by weakening or opening of the diaphragm, causing acid reflux. Although you can trust your primary care or gastroenterology that may have informed you of your hernia, you too must have a basic understanding of the problem. On that note, we present an overview of Hiatal Hernia, including its causes and treatment options. Read on.
Causes
Hernias are caused by a weakening or opening of the diaphragm. Simply put, the condition develops when the stomach moves above the diaphragm. There are many types of hernias, such as ventral, umbilical, epigastric, sports, femoral, and inguinal hernias. As their names suggest, each is dependent on where it develops.
Symptoms
Common symptoms of Hiatal Hernia include heartburn, difficulty in swallowing, and belching. In some cases, medication offers relief to the symptoms. The symptoms may include increased pressure on the abdomen, which can be due to obesity, coughing, pregnancy, or straining from a bowel movement. Some people are born with a larger than usual hiatus (space in the diaphragm through which the esophagus passes), which increases their susceptibility to developing a hiatal hernia. An injury could also be a cause. In addition, pregnant women and overweight people are at a high risk of developing the disorder.
Treatment
Hiatal Hernia symptoms can be sometimes treated through medication with the use of antacids or other medicines that reduce acid production. Another way of dealing with a hiatal hernia is by making lifestyle changes, such as having smaller meals several times a day, avoiding foods that can trigger heartburn, commitment to losing weight, and avoiding alcohol and smoking.
If the first line of treatment doesn’t help, the doctor may recommend Hiatal Hernia surgery. Most patients get to this point when it’s an emergency or they are not getting relief from medication. The Hiatal Hernia surgery involves pulling the stomach further down the abdominal cavity and making the diaphragm opening smaller, removing the hernia sac, and reconstructing the weak esophageal sphincter.
Recovery
Oftentimes, these procedures can be performed on an outpatient basis. There may be restrictions on food post-surgery depending on how the lower esophageal sphincter is strengthen, and the patient can resume their normal activities in a week. Complete recovery takes 2 to 3 weeks, but patients must avoid heavy lifting for at least 90 days after the procedure.
Need a Hernia Surgeon in Dallas or Fort Worth?
For proper treatment of hiatal hernia, it is important to choose an experienced Hernia surgeon with proven competence in performing Hiatal Hernia surgery. That is when you can trust a name such as DFW Bariatrics and General Surgery. To consult a Hernia surgeon in the Dallas Fort Worth area, book an appointment online or simply call 469-620-0222.
